Search engine optimization (SEO) is essential if you want your website to be easily discoverable. By following SEO best practices, you can improve the ranking of your webpages on search engine results pages (SERPs), which can lead to increased traffic, engagement and conversions. Whether you're a seasoned SEO professional or just getting started, this guide provides tips and best practices for optimizing your website and improving its visibility in search engines. Brand new to SEO? Read Google's SEO Starter Guide.
Search Engine Optimization Glossary
SEO key terms are bolded. Find full definitions of these terms in our SEO Glossary.
Keywords
Keywords are the bread and butter of SEO. A keyword is the main idea your content is about. If someone were to search for your article, this is likely the word or phrase they would put in a search box.
Keyword length matters
Package short and long keywords together for the best chance to have your content seen by the biggest audience. Keyword maps are helpful tools for this.
Use primary and secondary keywords
Your primary keyword should be in your:
- URL
- Title
- Meta description
- Body content
It should also be in some headers, image names and alt text.
Try to also include secondary keywords in your content. But make sure your primary keyword is your highest priority and captures your main idea.
Avoid keyword stuffing
Don't use a keyword too much. Search engines will penalize keyword stuffing — when you use a keyword an unusually high amount of times to manipulate a page or site's ranking in search. Doing this could get your website banned.

Content that sounds natural ranks higher in search results. Basically, if it doesn't sound like a human said it, don't say it.
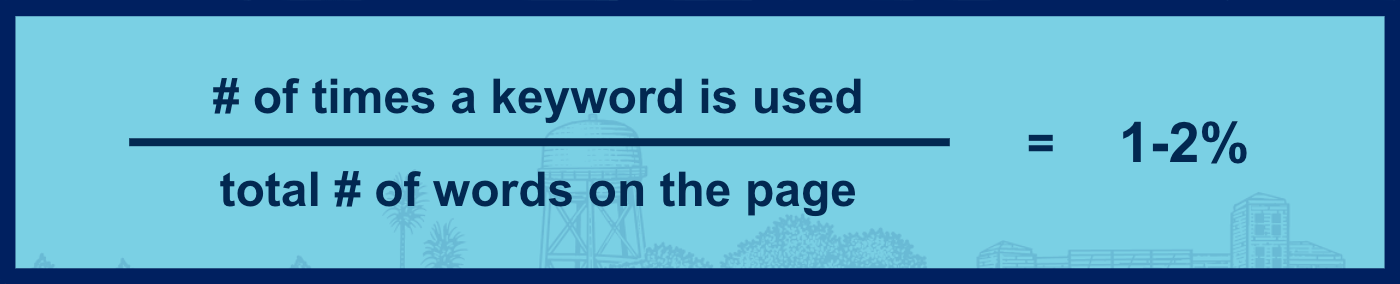
Keyword stuffing equation
Use this equation to make sure you're not keyword stuffing. If your result is higher than two percent, consider deleting some uses of the keyword or using synonyms.
Ranking
It's important to optimize your content to give it the best chance of ranking highly on SERPs. The higher your content ranks, the more page views it will get. A good goal is to shoot for the top 10 search results for your target keyword.
If you're interested in learning more, see how Google ranks webpages. This can inform how your pages are ranked in other search engines as well.
Search results
Google search results come in different forms (like standard, featured and rich snippets). These results contain important information about your page, so optimizing them is key to improving your ranking.
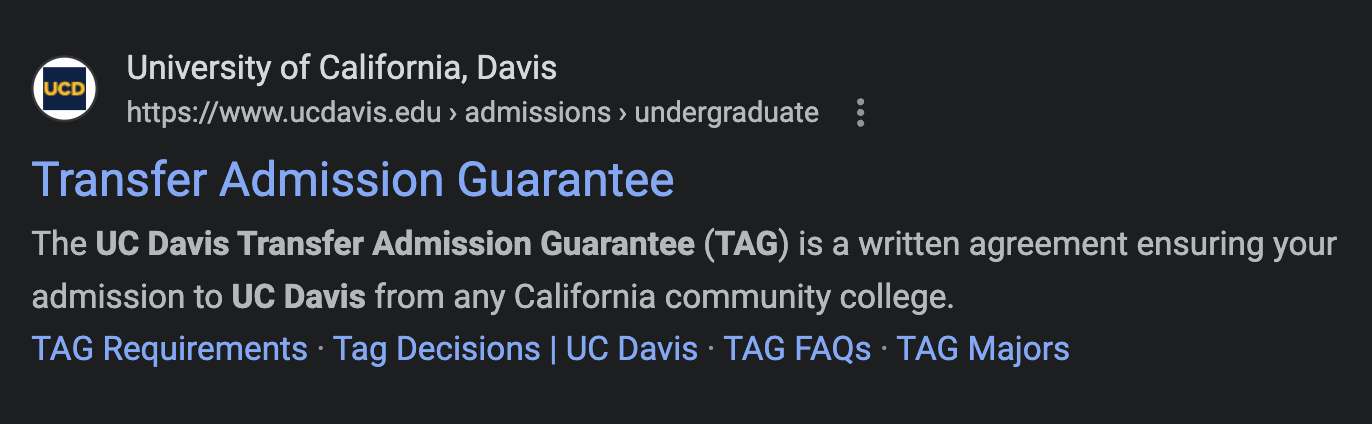
Standard snippets
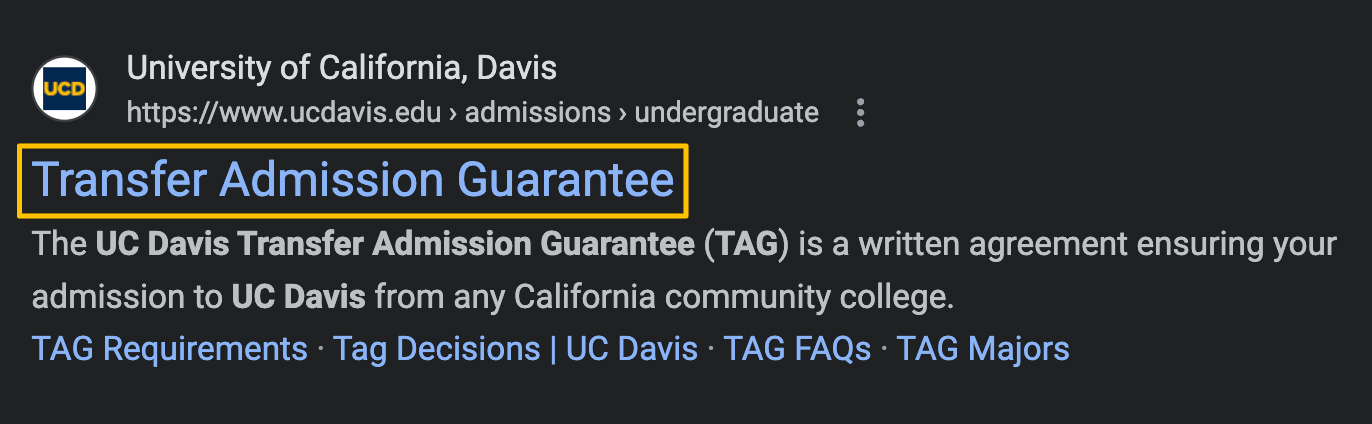
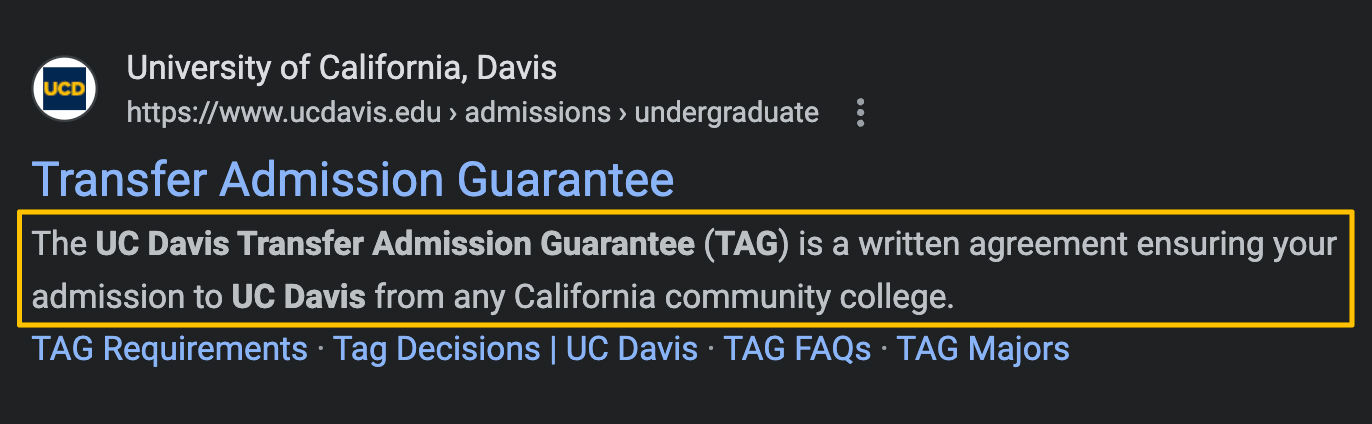
Standard snippets are what most people think of when they imagine search results. Each component of the snippet can be optimized.
- Brand and URL: https://www.ucdavis.edu > admissions > undergraduate
- Title tag: Transfer Admission Guarantee
- Meta description: The UC Davis Transfer Admission Guarantee (TAG) is a written agreement ensuring your admission to UC Davis from any California community college.
- Rich results: TAG Requirements · Tag Decisions | UC Davis · TAG FAQs · TAG Majors
URL
Keep your URL simple. URLs over 100 characters are often not indexed by search engines.
Make sure your primary keyword is in your URL. Search engines will take this into consideration when ranking your page, and if people search for your primary keyword, it will appear bolded in search results.
Use the most optimized URL when first publishing your content. Do not change your URL after publishing. This could tank your SEO.
URL examples
Say you were creating a URL for a page about heat domes.
Unoptimized: www.ucdavis.edu/climate-change-global-warming-extreme-temperatures-heat-dome-heat-wave-best-definition
- This URL contains relevant keywords, but it's too long (over 100 characters).
Unoptimized: www.ucdavis.edu/definitions
- This URL does meet the character limit, but it does not contain relevant keywords.
Optimized: www.ucdavis.edu/heat-dome
- This URL is under 100 characters and contains relevant keywords.
Keep in mind that you need to use the correct path to place your page in the right place on your site. If you wanted to put your heat domes page in the climate definitions section of your site, the URL would look like this: https://www.ucdavis.edu/climate/definitions/heat-dome. Ideally, the pages in the path also have relevant keywords for your page.
Redirects
- When reorganizing or merging content, make sure to redirect to the proper URL.
- Watch 404 logs to fix broken links or redirect where necessary.
- If deleting a page, find a page that provides similar content. If no page exists that is related, leave the page a 404. However, if you delete a page and are seeing traffic to it, you may want to consider creating a page to address the need.
Title tag
A title tag or page title is what shows up as the title of your page in search results. A title tag is not the same as a headline. A headline is the title seen on the webpage.
Your title tag is very important to optimize since this is what users will read first in search results. It also affects a page’s search rank.
Your title tag should be 55-60 characters long. Too few characters, and you miss an opportunity to use a good keyword. Too many characters, and your title tag will get cut off. Your headline can be longer than 60 characters, though.
It is best practice and accessible to put your brand name at the end of every title tag. Fortunately, SiteFarm automatically does this. Just make sure your final title tag does not exceed 60 characters with the brand name included.
Your title tag and headline should look similar. It's considered bad user experience to be taken to a page with a very different headline, and search engines are likely to penalize you for it by lowering your page's ranking. You should include your target keyword in both the headline and title tag to avoid confusion for the user as well as the search engine.
Google won't always show your title tag in search results if it determines your title tag inaccurately reflects what is on your page. Review how Google deals with title tag issues to avoid having your custom title tag changed.
Meta description
A meta description is the summary of your content that appears in search results below your title tag
Your meta description should be 155-160 characters long. Start with a call to action, include relevant keywords and don't go over the character limit so your description doesn't get cut off.
Even though Google will not use your meta description to determine your page's ranking, it's still important to use keywords here. When people search for your keywords, they will appear in bold letters in search results, which encourages users to choose your content.
Google won't always show your meta description in search results depending on the search query. Instead, Google will show text from the webpage that best answers the user's search query. Be sure to write unique meta descriptions that best describe the content of your pages to encourage Google to show your custom description.
Content
High-quality, unique, useful content is what search engines are looking for and will rank highly. Always try to write 10x content. This is content that is 10x better than the highest-ranked content in search engine results.
Use your target keyword and synonyms of that keyword in your body paragraphs.
Try to stay above 300 words, but don’t focus too much on word count. What matters more is whether or not you are providing relevant content that answers people’s questions.
You can look up the most frequently searched for questions about your topic using tools like Answer the Public. You can also get a good idea of what people are searching for by observing Google’s autocomplete suggestions.
Useful content
By building content that fulfills a user's need, you have a better chance at ranking in search. If you are a reputable source for the topic, are providing a better experience than competition and/or are addressing a niche that is not currently being addressed, you are more likely to rank highly in search results.
Useful content tips
- Focus on topics you are known for or craft a unique and valuable experience for your users.
- Build content that is evergreen or seasonal.
- Use metrics to make the best decisions in optimizing existing content or in crafting new content.
Header tags
Header tags or heading tags are the titles and subtitles of your webpage. They break up content into scannable chunks. Header tags are important because they help readers scan your content and learn information more quickly.
Search engines scan header tags to determine a page's ranking, so be sure to include your target primary and secondary keywords whenever relevant.
Header tags are categorized as H1, H2, H3, H4, and H5 with descending levels of size and importance. Every page should have only one H1.
For accessibility and SEO reasons, header tags should go in order and should not skip ahead. View UC Davis' web accessibility page for examples.
Duplicate content
Sometimes departments will republish another department's article, creating duplicate content.
Search engines try not to index duplicate content, so if duplicate content exists, search engines will choose only one page to show in search results. However, it might not choose to show the original page.
Canonical tags
A canonical tag tells search engines to show only one version of the page. By using a canonical tag, you're making sure search engines aren't confused and knows to show the original version in search results.
- When publishing new, original content:
- Put your content's URL in the "Canonical URL" section of your page. This is known as a self-referential canonical tag.
- When duplicating someone else's content:
- Put the original content's URL in the "Canonical URL" section of your page.
Don't be afraid to ask publishers who are duplicating your content to use a canonical tag to tell search engines to prioritize the original.
In some cases (like if the duplicator's website tends to get more views), you may choose to use a canonical tag to tell search engines to show the duplicate content in search results instead.
Read the full Canonical Tags Guide
Images
Choose images that are relevant to your content so that your image names and alt tags can include your target keyword or synonyms of it. Search engines will crawl the names of your images, so be sure to name your files appropriately. Avoid using images that are purely decorative.
Include your primary keyword when applicable, separate words by dashes (not underscores) and try to keep the file name under 10 words. Use more specific keywords at the beginning of the name and general, branded keywords at the end.
Examples:
-
cow-emissions-climate-uc-davis.jpg
-
john-doe-professor-climate-uc-davis.jpg
File names and alt tags
Alt tags are also important for SEO. An alt tag is text describing an image, which is read aloud by screen readers and appears when the image does not load. View UC Davis' web accessibility page for a good example of an alt tag.
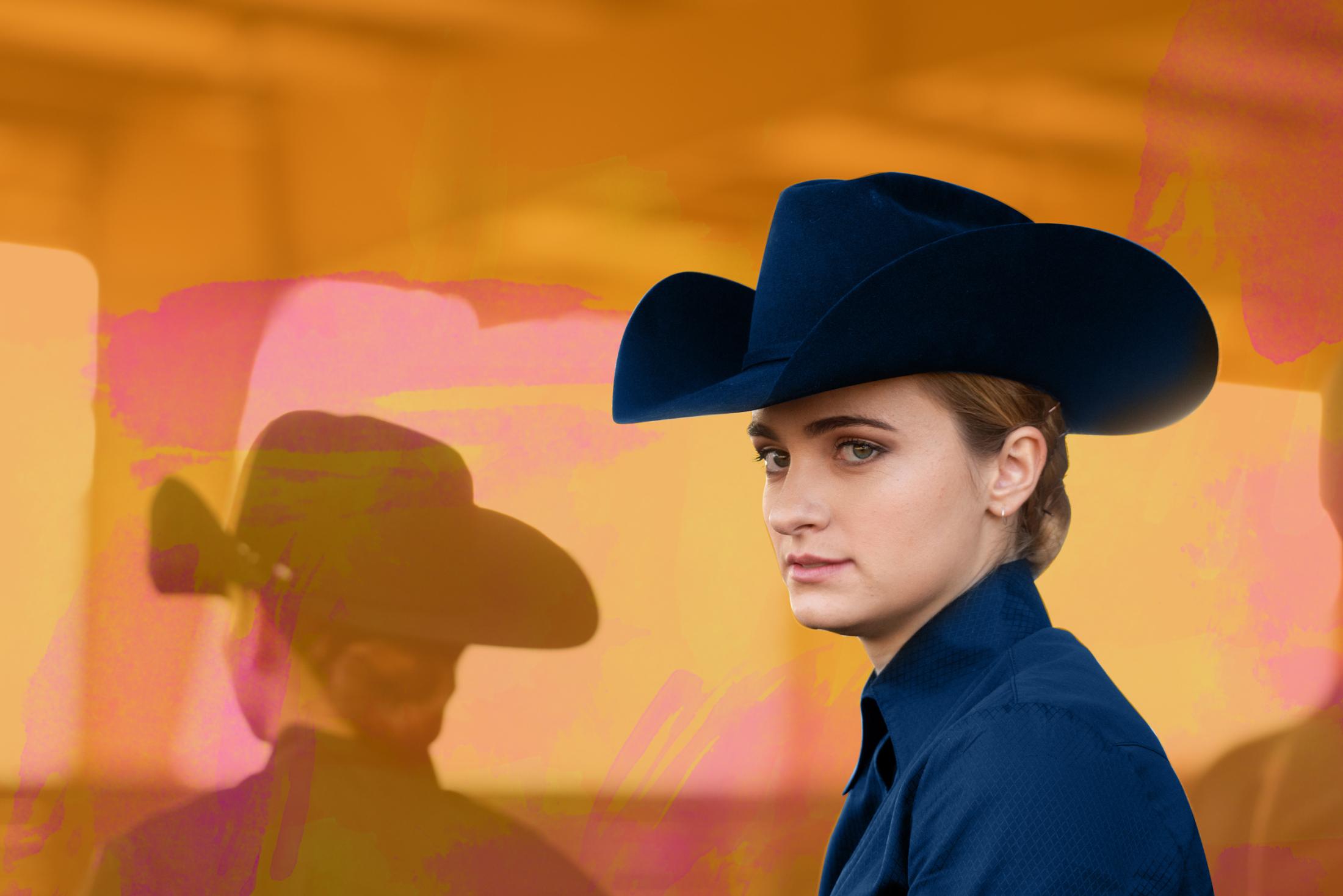

On our brand guide website, this image is named brand-guide-hero_2.jpeg, and the alt text is "Young woman in a cowboy hat."
To best optimize an image, insert keywords in the file name and alt tag. All images should have “UC Davis” in both their title and alt tag.
The name should go from specific to general.
- Optimized image name: cowboy-hat-student-brand-guide-uc-davis.jpeg.
- Optimized alt tag: UC Davis student in a dark blue cowboy hat against a vibrant orange and pink background
Indexing
Search engines crawl sites and pages to index them so that they will show up in search results.
It can take a few hours to a few weeks for a new page to be indexed. Just because a page is indexed does not mean it will get a high ranking. Pages that consistently rank low can be removed from the index.
There is no guarantee that search engines will index a page. Search engines will often not index duplicate content or images, content it considers not useful and URLs that have too many parameters.
Indexing tips
To speed up indexing, be sure to:
- Have a fast server so there's no overload
- Link to new pages in more prominent places (like the homepage or landing pages)
- Avoid using unnecessary URLs (like category filters)
- Use sitemaps to help search engines identify new URLs
Most importantly, always aim for high-quality, useful content. Search engines will prioritize this type of content when choosing what to index and when. Watch Google's indexing video to learn more.
SEO in SiteFarm
When choosing a content management system, built-in SEO functionality is important. Fortunately, UC Davis' SiteFarm CMS makes search engine optimization easy.
